Who Is a Good Candidate for Piles Treatment?
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, affect many individuals due to lifestyle habits, bowel irregularities, and increased pressure on the rectal region. People in Thrissur often seek clear information about who may benefit from piles treatment in order to recognize symptoms early and choose appropriate care options. Not everyone with hemorrhoids requires medical procedures, but certain signs and conditions indicate when treatment may be necessary.
Understanding candidacy for piles treatment involves evaluating symptoms, severity, daily impact, response to conservative care, and overall health status. This helps individuals determine whether lifestyle management alone is sufficient or if medical intervention should be considered.
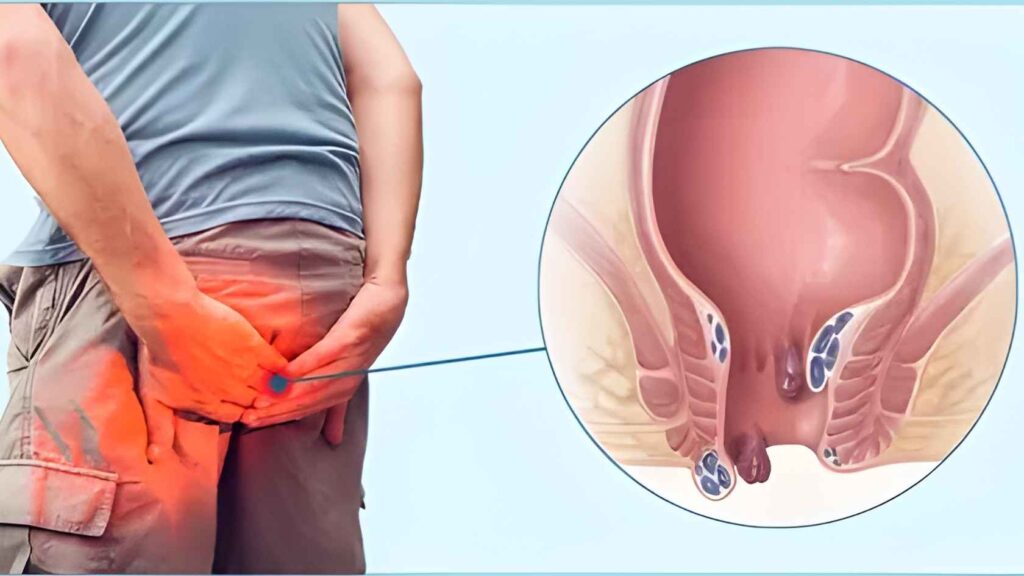
1. Individuals With Persistent Symptoms
One of the primary indicators for piles treatment is the presence of ongoing symptoms that do not improve with basic home care.
Ongoing Pain and Discomfort
People who experience continuous pain, burning sensations, or discomfort while sitting or during bowel movements may be suitable candidates for treatment. Persistent pain often indicates inflamed or advanced hemorrhoids that require medical attention.
Regular Rectal Bleeding
Occasional mild bleeding may occur in early hemorrhoids. However, frequent or continuous bleeding is a sign that professional evaluation is needed. Individuals with repeated bleeding episodes are often advised to consider appropriate treatment options to prevent complications such as anemia.
Chronic Itching and Irritation
Constant itching, irritation, or skin inflammation around the anal region may suggest ongoing hemorrhoidal activity. When topical remedies and hygiene measures fail to provide relief, further treatment may be beneficial.
2. People With Advanced Stages of Hemorrhoids
The severity of hemorrhoids plays a major role in determining treatment candidacy.
Prolapsed Internal Hemorrhoids
Individuals with hemorrhoids that protrude outside the anus during bowel movements and do not return on their own may require medical intervention. Manual repositioning or persistent prolapse often indicates moderate to advanced disease stages.
Permanently Prolapsed Hemorrhoids
When hemorrhoids remain outside the anus and cannot be pushed back, they may cause discomfort, hygiene difficulties, and increased infection risk. Such cases are commonly considered for procedural treatment.
Large External Hemorrhoids
People with large, swollen external hemorrhoids that interfere with daily activities may benefit from targeted medical management.
3. Patients With Recurrent Hemorrhoids
Some individuals experience repeated episodes of piles despite lifestyle modifications.
Frequent Flare-Ups
Those who develop hemorrhoids multiple times a year may be suitable candidates for further evaluation and treatment. Recurring flare-ups often indicate underlying issues that need structured management.
Poor Response to Home Remedies
When dietary changes, hydration, topical applications, and sitz baths do not provide lasting relief, additional treatment options may be required. Persistent symptoms despite conservative care are a common reason for seeking medical intervention.
4. Individuals With Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors
Certain lifestyle patterns increase the likelihood of requiring piles treatment.
Sedentary Lifestyle
People who sit for prolonged periods, especially at work or during travel, may develop increased pressure in the rectal area. When symptoms persist despite posture changes and activity improvements, treatment may be necessary.
Low-Fiber Diet Habits
Individuals with ongoing constipation due to inadequate fiber intake may develop recurring hemorrhoids. If dietary improvements fail to regulate bowel habits, medical treatment may be recommended.
Occupations Involving Heavy Lifting
Jobs that require frequent heavy lifting can increase abdominal pressure, contributing to hemorrhoid development. Repeated strain may make professional treatment necessary.
5. Pregnant and Postpartum Individuals
Pregnancy-related hormonal changes and pressure on pelvic veins often increase the risk of hemorrhoids.
Pregnancy-Associated Hemorrhoids
Some pregnant individuals experience hemorrhoids that do not resolve after childbirth. Persistent symptoms after delivery may indicate the need for medical management.
Postpartum Hemorrhoids
Those who continue to experience pain, bleeding, or swelling after childbirth may be suitable candidates for treatment, especially when conservative measures are ineffective.
6. Older Adults With Tissue Weakness
Age-related changes in connective tissues can affect vein support.
Reduced Tissue Elasticity
As people age, the tissues supporting rectal veins may weaken, making hemorrhoids more likely to develop or worsen. Older adults with persistent symptoms may benefit from professional treatment approaches.
Chronic Medical Conditions
Certain health conditions that affect bowel movements or circulation may increase the likelihood of hemorrhoid formation. In such cases, treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s overall health status.
7. Individuals With Complications From Piles
Complications are strong indicators for medical intervention.
Thrombosed Hemorrhoids
When blood clots form within external hemorrhoids, severe pain and swelling can occur. Individuals experiencing thrombosis often require prompt treatment to relieve symptoms and prevent further issues.
Anemia Due to Blood Loss
Chronic bleeding from hemorrhoids can lead to reduced red blood cell levels. People with anemia related to piles are commonly advised to seek treatment to address the root cause.
Infection and Inflammation
Although uncommon, infected hemorrhoids can cause fever, discharge, and severe discomfort. Such cases typically require professional medical care.
8. People Experiencing Reduced Quality of Life
Piles can significantly affect daily comfort and routine activities.
Difficulty Sitting or Walking
Individuals who struggle to sit comfortably or walk due to hemorrhoid-related pain may benefit from treatment aimed at symptom relief.
Sleep Disturbances
Night-time discomfort or itching can interfere with sleep. Persistent symptoms affecting rest and recovery may indicate the need for medical evaluation.
Emotional Stress and Discomfort
Ongoing symptoms can cause embarrassment, stress, and anxiety. People experiencing emotional strain due to piles may consider treatment to improve overall well-being.
9. Candidates Based on Diagnostic Evaluation
Medical assessment helps determine suitability for treatment.
Clinical Examination Findings
Healthcare professionals evaluate hemorrhoid size, location, and severity during physical examination. Based on these findings, individuals may be classified as suitable candidates for different treatment options.
Additional Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, further tests are recommended to rule out other causes of rectal bleeding. Individuals with confirmed hemorrhoidal disease after evaluation may proceed with appropriate treatment planning.
10. Individuals Seeking Preventive Intervention
Some people consider treatment to prevent worsening of symptoms.
Early Intervention for Moderate Symptoms
Those with moderate hemorrhoids who want to avoid disease progression may choose treatment options to reduce future complications.
Preventing Recurrence
Individuals with a history of repeated hemorrhoids may consider medical intervention to reduce recurrence risk and maintain long-term comfort.
11. Situations Where Immediate Treatment Is Recommended
Certain symptoms require prompt attention.
Sudden Severe Pain
Acute pain that develops rapidly may indicate thrombosis or strangulated hemorrhoids. Immediate evaluation and treatment are often necessary.
Heavy or Continuous Bleeding
Ongoing bleeding should not be ignored and requires medical assessment to identify the cause and determine suitable treatment.
Prolapse With Severe Swelling
Large prolapsed hemorrhoids with swelling and irritation may require urgent care to prevent complications.
12. Final Overview
A good candidate for piles treatment is someone who experiences persistent symptoms, advanced hemorrhoid stages, recurring flare-ups, or complications that interfere with daily life. Lifestyle factors, pregnancy-related changes, age-related tissue weakness, and overall health conditions also influence treatment suitability. Early recognition and proper evaluation allow individuals to choose appropriate management options and improve comfort. For those seeking guidance in Thrissur, understanding candidacy criteria helps support timely decision-making and better long-term health outcomes.
Table Of Content
Introduction
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are swollen blood vessels in the anal or rectal area that can cause pain, itching, or bleeding. Learn more
Cost
The cost of piles treatment in Thrissur varies depending on the treatment method, disease severity, hospital facilities, and postoperative care needs. Learn more
Consultation
During the consultation, the doctor evaluates symptoms, performs a clinical examination, reviews medical history, and discusses suitable treatment options. Learn more
Questions
You should ask about treatment methods, recovery time, possible risks, expected results, and follow-up care. Learn more
Risks and safety
Piles treatment is generally safe when properly performed, though risks may include pain, bleeding, infection, or recurrence. Learn more
Preparation
Preparation includes medical evaluation, medication adjustments, dietary guidance, bowel preparation if required, and planning postoperative care. Learn more
Steps
The procedure typically includes anesthesia, removal or reduction of hemorrhoidal tissue, bleeding control, and postoperative monitoring. Learn more
Recovery
Recovery usually involves gradual pain reduction, wound healing, bowel habit regulation, and return to daily activities over time. Learn more
Results
Results often include relief from pain and bleeding, improved comfort during bowel movements, and better quality of life. Learn more
Before-and-after
Before-and-after results commonly show reduced swelling, symptom improvement, and restoration of normal anal function. Learn more
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Who is considered a good candidate for piles treatment?
Individuals with persistent symptoms such as pain, bleeding, or swelling that do not improve with home care are considered good candidates for piles treatment.
2. Do all people with piles need medical treatment?
No, mild piles may improve with lifestyle changes, but treatment is recommended when symptoms become severe or long-lasting.
3. When should I consider treatment for piles?
Treatment should be considered if symptoms such as bleeding, pain, or prolapse continue despite dietary and lifestyle modifications.
4. Are people with prolapsed hemorrhoids suitable for treatment?
Yes, individuals with prolapsed hemorrhoids that do not return inside the anus on their own often require medical intervention.
5. Can recurring piles make someone a candidate for treatment?
Yes, frequent recurrence of piles may indicate the need for professional treatment to prevent further episodes.
6. Are older adults more likely to need piles treatment?
Older adults may be more likely to require treatment due to weakened supportive tissues and ongoing symptoms.
7. Can lifestyle factors affect eligibility for piles treatment?
Yes, prolonged sitting, low-fiber diets, and heavy lifting can increase symptom severity and the need for treatment.
8. Do pregnant or postpartum individuals need piles treatment?
Some pregnant or postpartum individuals may require treatment if symptoms persist after delivery and do not improve with basic care.
9. Is piles treatment recommended for people with complications?
Yes, individuals with complications such as thrombosis, anemia from bleeding, or infection are strong candidates for treatment.
10. How is eligibility for piles treatment determined?
Eligibility is usually based on symptom severity, physical examination findings, response to conservative care, and overall health condition.